What Does Doxycycline Treat?

Doxycycline is a tetracycline antibiotic commonly prescribed to fight a wide range of infections. But with so many antibiotics available, what makes doxycycline stand out? Let’s explore what doxycycline treats and why it might be the right choice for you.
Battling Bacteria: Doxycycline’s Targets
Buy Doxycycline Online works by stopping the growth of bacteria. This makes it effective against a variety of infections, including:
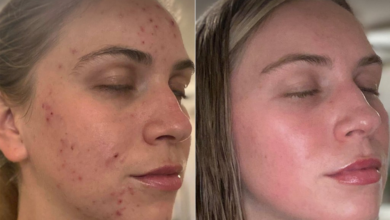
- Acne: Doxycycline is commonly prescribe to treat acne, especially in cases where other treatments have failed. It helps reduce inflammation and bacterial growth associated with acne.
- Bacterial Infections: This medication is used to treat various bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, and certain sexually transmitted infections like chlamydia and gonorrhea.
- Lyme Disease: Doxycycline is often prescribe to treat early-stage Lyme disease caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi. It can also help prevent Lyme disease if taken after a tick bite in certain areas where Lyme disease is prevalent.
- Malaria: In combination with other medications, it is use to prevent malaria in travelers to malaria-endemic areas. It is not effective in treating malaria infections.
- Rosacea: Doxycycline may be prescribe to manage the symptoms of rosacea, a chronic skin condition characterized by facial redness, bumps, and pimples.
- Periodontitis: In cases of severe gum disease (periodontitis), it may be used as an adjunct to scaling and root planing to help reduce pocket depth and improve gum health.
Important Note: Doxycycline, like all antibiotics, is ineffective against viruses. So, it won’t help with the common cold or flu.
Beyond Antibiotics: Doxycycline’s Additional Uses
In some cases, it is use for purposes other than fighting bacterial infections. For instance, it can help with:
- Severe acne: Doxycycline can be a valuable tool in managing severe acne alongside other treatments.
- Gum disease (periodontitis): The Medicine, along with proper dental hygiene practices, can help reduce inflammation and improve gum health.
Considering Doxycycline: Talking to Your Doctor
Doxycycline is a powerful medication, and it’s not always the right choice for everyone. Here’s why consulting your doctor is crucial:
- Finding the right fit: Your doctor will determine if it is the most suitable antibiotic for your specific infection.
- Dosage and duration: The appropriate dosage and treatment duration will depend on the type and severity of your infection.
- Drug interactions: Doxycycline can interact with other medications. Be sure to tell your doctor about all the medications and supplements you’re taking.
Side Effects of Doxycycline
Like all medications, it can cause side effects. Common side effects may include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Sun sensitivity (increased risk of sunburn)
- Vaginal yeast infections (in women)
In rare cases, doxycycline can cause more serious side effects, such as severe headache, blurred vision, difficulty swallowing, or chest pain. If you experience any of these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
Precautions and Considerations
- Doxycycline should not be take by pregnant women or children under the age of 8, as it can cause permanent discoloration of teeth and affect bone development.
- It is important to avoid taking it with dairy products, antacids, or iron supplements, as these can interfere with its absorption.
- Inform your healthcare provider about any other medications you are taking, as they may interact with doxycycline.
Remember: Never take this pill without a prescription, and always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully.